Cellular Respiration: Chemiosmosis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCellular Respiration: Chemiosmosis definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
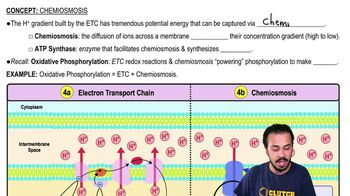
- ChemiosmosisDiffusion of ions across a semipermeable membrane, driven by a concentration gradient established by the electron transport chain.
- Electron Transport ChainA series of redox reactions that build a hydrogen ion concentration gradient, crucial for ATP production.
- Hydrogen Ion Concentration GradientA difference in hydrogen ion concentration across a membrane, storing potential energy for ATP synthesis.
- ATP SynthaseAn enzyme that facilitates the synthesis of ATP by allowing hydrogen ions to diffuse down their concentration gradient.
- Oxidative PhosphorylationA process that uses the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis to produce ATP during aerobic respiration.
- NADHAn electron carrier that donates electrons to the electron transport chain, aiding in ATP production.
- FADH2An electron carrier that transfers electrons to the electron transport chain, contributing to the hydrogen ion gradient.
- Intermembrane SpaceThe area between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes where hydrogen ions accumulate.
- Mitochondrial MatrixThe innermost compartment of the mitochondrion, where the hydrogen ion concentration is lower.
- Redox ReactionsChemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons, crucial for the electron transport chain.
- Oxygen GasThe final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, forming water as a byproduct.
- PhosphorylationThe addition of a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP, powered by the hydrogen ion gradient.
- Aerobic RespirationA process of energy production in cells that requires oxygen and produces ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
- Semipermeable MembraneA membrane that allows certain ions or molecules to pass through, essential for chemiosmosis.
- Potential EnergyStored energy in the hydrogen ion concentration gradient, used to drive ATP synthesis.