Adaptation of Sensory Receptors definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackAdaptation of Sensory Receptors definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
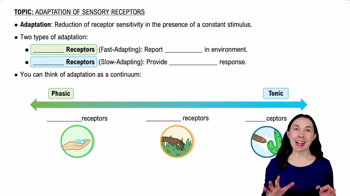
- AdaptationReduction in receptor sensitivity to a constant stimulus, conserving energy and maintaining neural health.
- Phasic ReceptorsFast adapting receptors that respond quickly to changes but reduce firing when the stimulus is constant.
- Tonic ReceptorsSlow adapting receptors that provide a sustained response even when the stimulus is constant.
- Peripheral Nervous SystemPart of the nervous system containing phasic and tonic receptors, responsible for sensory adaptation.
- ThermoreceptorsReceptors that detect temperature changes, exhibiting both phasic and tonic properties.
- NociceptorsPain receptors that provide a sustained response, crucial for awareness and behavioral adjustment.
- ProprioceptorsReceptors providing information about body position and movement, essential for spatial navigation.
- MechanoreceptorsReceptors responding to pressure and vibration, exhibiting both phasic and tonic properties.
- Neural HealthState of the nervous system maintained by adaptation, preventing constant neuron firing.
- StimulusAn external factor that receptors respond to, which can be constant or changing.