12. The Central Nervous System
The Cerebrum
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
The brain is divided into two cerebral hemispheres by the ________________.
2317views53rank - Multiple Choice
The occipital lobe is found at the ________ of the brain, while the parietal lobe is found at the ________.
2005views36rank - Multiple Choice
A spinal reflex is a rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus. Tala has an issue with motor areas of her brain. Will her spinal reflexes still function?
2098views53rank - Multiple Choice
Which of the following body parts would you expect to have the greatest size difference between its area on the motor homunculus and its area on the sensory homunculus?
1714views43rank - Textbook Question
a. Make a rough drawing of the lateral aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere.
b. You may be thinking, 'But I just can't draw!' So, name the hemisphere involved with most people's ability to draw.
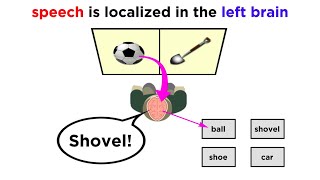
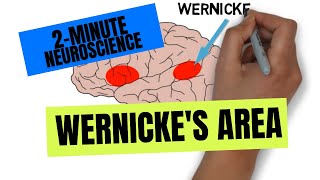
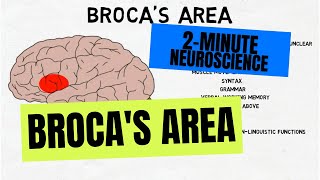
c. On your drawing, locate the following areas and provide the major function of each: primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, somatosensory association cortex, primary somatosensory cortex, visual and auditory areas, prefrontal cortex, Wernicke's and Broca's areas.
956views - Textbook Question
The only cranial nerves that are attached to the cerebrum are the____ nerves.
(a) optic
(b) oculomotor
(c) trochlear
(d) olfactory
(e) abducens
1535views - Textbook Question
Mark the following statements about the brain as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
The cerebrum is responsible for our basic, involuntary functions and reflexes.
731views - Textbook Question
Which statement about cerebral white matter is false?
a. Commissural fibers connect the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
b. Projection fibers connect the cerebral cortex of one hemisphere with structures in the other hemisphere.
c. The corpus callosum is the largest bundle of white matter in the brain.
d. Association fibers connect the gyri of the cerebral cortex with one another.
756views