Choosing the right graded readers for young learners
Picking out the right graded readers for your young learners takes a little thought. There are thousands and thousands of stories out there. Not only do you have to find the right level but also a range of books that will keep them captivated as they learn to read.
In this brief guide, I’ll be helping you to choose the right Disney Kids Readers for your students, so they can participate in guided and independent reading in class and at home.
Let’s delve in.
First, what’s the difference between guided and independent reading?
Guided reading
In class, students typically read aloud in a small group with a teacher. The teacher supports the children as they decode the words, navigate elements of pronunciation, and make sense of the meaning. At home, a child reads aloud to a parent or caregiver. This is a terrific way to involve parents in a child’s path toward reading fluency.
Independent reading
Independent reading, on the other hand, is when students read silently to themselves. These students are already reading with some confidence. They can decode common words and have a good handle on sight words. Their reading speed is fluent enough to focus on the meaning of the text.
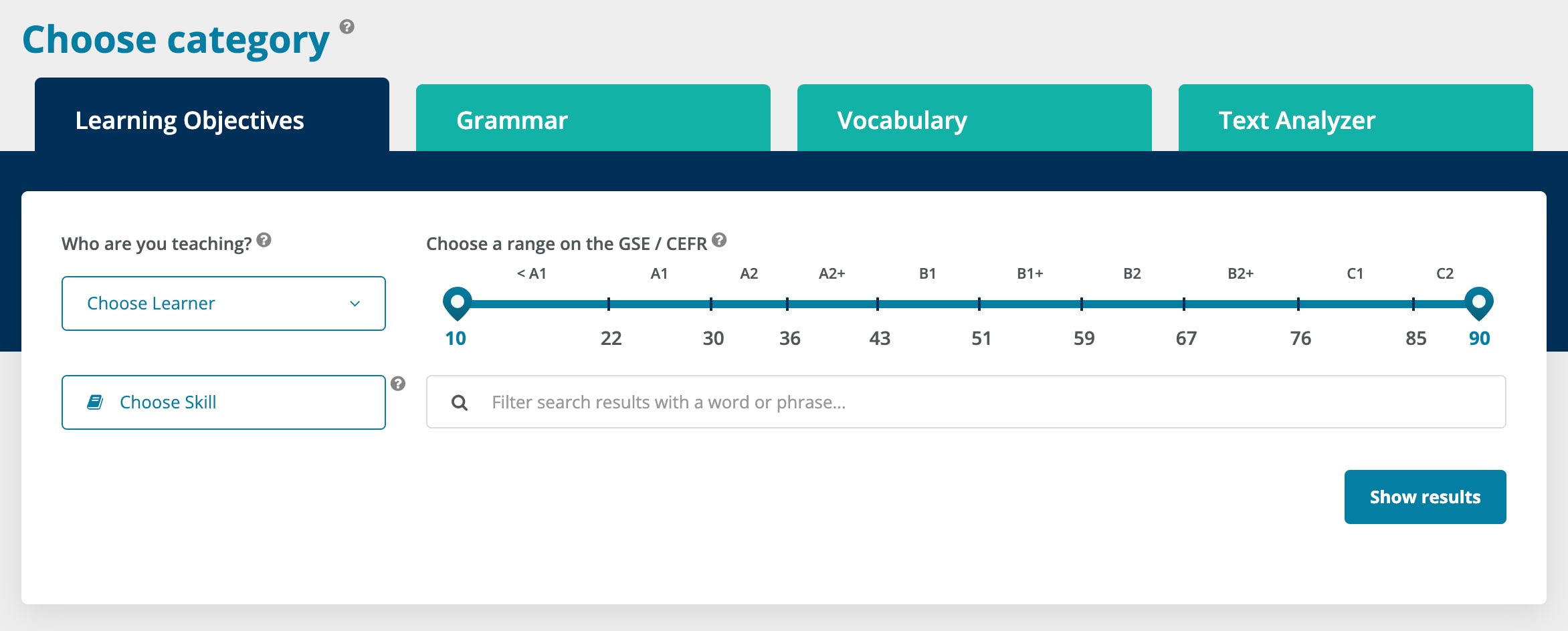
Graded readers can help with leveling
So, how do you know which reader to choose for your students? Well, graded readers are already organized by level. They also often provide metrics to help teachers make informed decisions about what reading level a child is at.
Let’s take a look at Disney Kids Readers as an example: