Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, 5th Edition, AP Edition © 2022
Randall D Knight

Physics for Scientists and Engineers incorporates Physics Education Research and cognitive science best practices that encourage conceptual development, problem-solving skill acquisition and visualization. Author Randall Knight stresses qualitative reasoning through physics principles and development of problem-solving skills using a systematic, scaffolded approach. This practical introduction to physics relates physics to everyday life and includes models, modeling and advanced topics.
New content in the 5th Edition includes Entropy quantitatively, Viscosity and Poiseuille's Equation, and Carnot Efficiency details.
Problem-solving skills
- Model boxes analyze complex, real-world situations to help students recognize when and how to use recurring models in solving problems.
Deeper understanding
- Looking Back Pointers direct students to the exact point in a previous chapter to use when they need to apply or review concepts.
- Visual chapter summaries are explicitly hierarchical in design to help students connect the ideas, organize their knowledge, and see the big picture.
A variety of physics topics
- Optional topics include rocket propulsion, gyroscopes and precession, wave equation including for electromagnetic waves, speed of sound in gases and interference of light.
- Tactics Boxes give step-by-step procedures for developing skills (drawing free-body diagrams, using ray tracing).
Problem-solving skills
- 4-step problem-solving approach shifts to Model/Visualize/Solve/Review, using a final step of “Review” rather than “Assess” to better reflect the content of the final step. This approach provides a framework throughout the book, using the 4-step framework with detailed problem-solving strategies for different topics and types of problems. Tactics Boxes give step-by-step procedures for developing specific skills (drawing free-body diagrams, using ray tracing, etc.).
- Worked examples follow the 4-step strategy and include careful explanations of the underlying, and often unstated, reasoning with new examples that show how things work to relate physics to everyday life.
Deeper understanding
- Enhanced Chapter Previews address the questions students are most likely to ask themselves while studying the material for the first time. Questions cover the important ideas and provide a big-picture overview of the chapter's key principles.
- Enhanced: 20% of Enhanced End-of-Chapter (EOC) questions and 300 EOC questions are coded with wrong-answer feedback. Revised EOC problem sets offer more challenging problems to expand the range of physics and math skills students use to solve problems.
- New: 10 Reading Questions per chapter, created by Randall Knight, provide wrong-answer feedback, check students' familiarity with key concepts and motivate them to do assigned reading before class.
- New: Interactive Prelecture Videos introduce key topics with embedded assessment to help students prepare before lecture and professors to identify student misconceptions. Expanded animated whiteboard prelecture videos provide active classroom content. Quantitative prelecture videos help students learn how to solve problems for a specific concept.
- New: Ready-to-Go Study Tools in the Study Area help students master the toughest topics. Students can use it on their own, even when their professor doesn't assign it.
- New: 25 Video Tutor Solutions, specific to the text, walk students through the problem-solving process and link to relevant content. All are available in the Study Area and assignable in Mastering.
- New: Book-specific Tutorials specific to each chapter of Physics for Scientists and Engineers are assignable in Mastering Physics.
- New: 25 Video Tutor Solutions (VTS) for Physics for Scientists and Engineers walk students through the problem-solving process, provide links to relevant content in the text, and can be accessed using embedded links in the eText. Select VTSs are provided as optional links in related end-of-chapter problems.
I. NEWTON’S LAWS
1. Concepts of Motion
2. Kinematics in One Dimension
3. Vectors and Coordinate Systems
4. Kinematics in Two Dimensions
5. Force and Motion
6. Dynamics I: Motion Along a Line
7. Newton’s Third Law
8. Dynamics II: Motion in a Plane
II. CONSERVATION LAWS
9. Work and Kinetic Energy
10. Interactions and Potential Energy
11. Impulse and Momentum
III. APPLICATIONS OF NEWTONIAN MECHANICS
12. Rotation of a Rigid Body
13. Newton’s Theory of Gravity
14. Fluids and Elasticity
IV. OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
15. Oscillations
16. Traveling Waves
17. Superposition
V. THERMODYNAMICS
18. A Macroscopic Description of Matter
19. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics
20. The Micro/Macro Connection
21. Heat Engines and Refrigerators
VI. ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
22. Electric Charges and Forces
23. The Electric Field
24. Gauss’s Law
25. The Electric Potential
26. Potential and Field
27. Current and Resistance
28. Fundamentals of Circuits
29. The Magnetic Field
30. Electromagnetic Induction
31. Electromagnetic Fields and Waves
32. AC Circuits
VII. OPTICS
33. Wave Optics
34. Ray Optics
35. Optical Instruments
VIII. RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM PHYSICS
36. Relativity
37. The Foundations of Modern Physics
38. Quantization
39. Wave Functions and Uncertainty
40. One-Dimensional Quantum Mechanics
41. Atomic Physics
42. Nuclear Physics
Appendix A Mathematics Review
Appendix B Periodic Table of Elements
Appendix C Atomic and Nuclear Data
Answers to Stop to Think Questions and Odd-Numbered Problems
Randy D Knight
California Polytechnic State University-San Luis Obispo
Randy Knight taught introductory physics for thirty-two years at Ohio State University and California Polytechnic State University, where he is Professor Emeritus of Physics. Professor Knight received a PhD in physics from the University of California, Berkeley, and was a post-doctoral fellow at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics before joining the faculty at Ohio State University. A growing awareness of the importance of research in physics education led first to Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach and later College Physics: A Strategic Approach. Professor Knight's research interests are in the fields of laser spectroscopy and environmental science. When he's not in front of a computer, you can find Randy hiking, traveling, playing the piano, or spending time with his wife Sally and their five cats.
This program is available in a variety of formats. You can review the individual prices for each ISBN in our catalog. All access codes are for use by 1 student, for 1 course, for up to 1 year, and are non-transferable.
| Format | ISBN-13 |
|---|---|
| AP Student Edition (HS binding) with Modified Mastering Physics with Pearson eTextbook (up to 6-Years) | 9780137302260 |
| Modified Mastering Physics with Pearson eTextbook (1-Year access) | 9780137452910 |
| Modified Mastering Physics with Pearson eTextbook (6-Year access) | 9780137452927 |

Not seeing what you’re looking for?
Check out our catalog
Review all our AP®, Honors, and Electives programs, including available formats, prices, and ISBNs
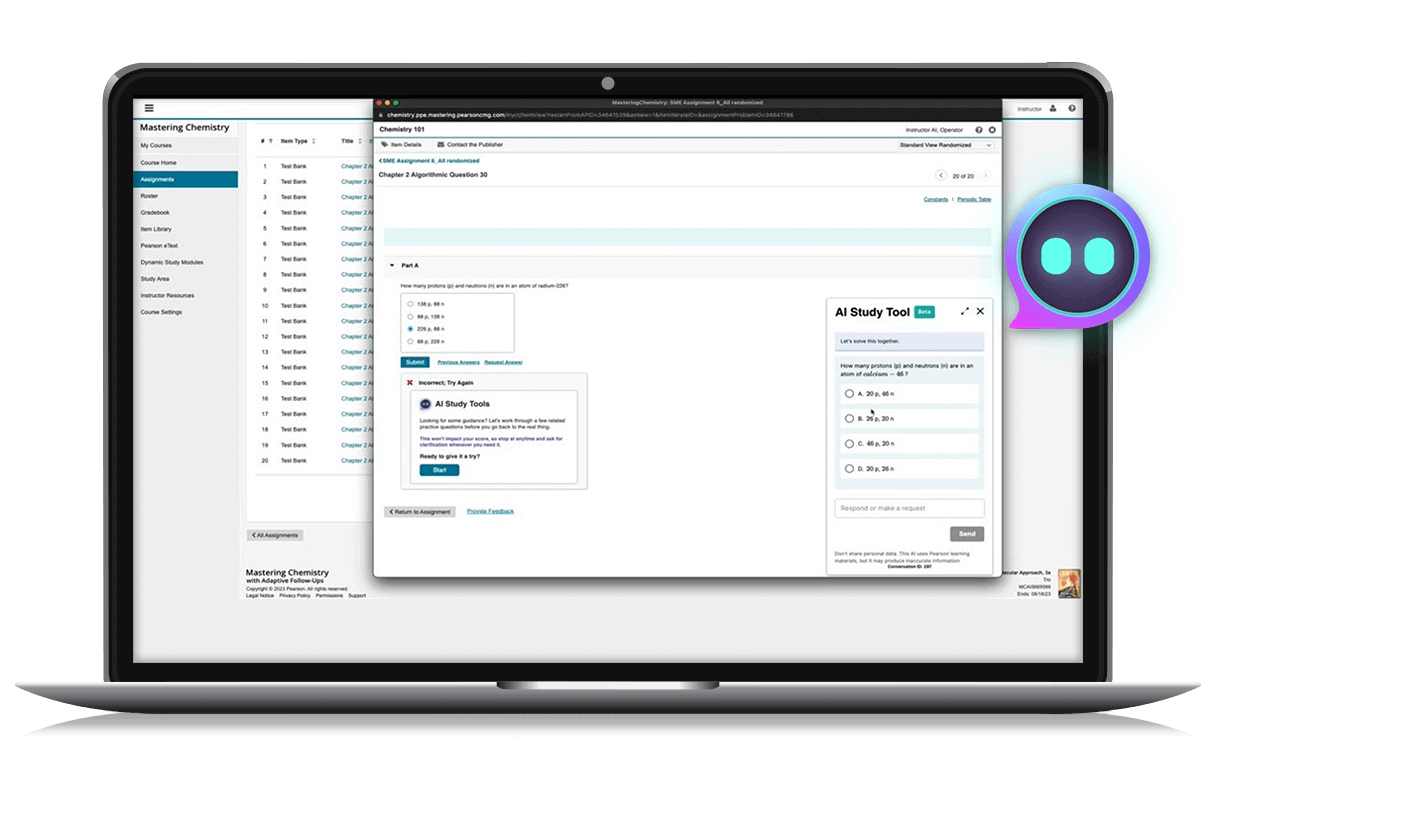
Online learning
Mastering
An immersive and adaptable online learning platform that empowers students to learn through active and engaging experiences. With personalized tutorials, analytics, and feedback, Mastering® helps high school students develop a strong foundation in science and engineering programs.
If you'd like to see a demo of Mastering, contact our team.
AP correlation
Our AP programs are correlated to the standardized exams offered by the College Board.

AP®, Honors, & Electives Catalog
Not seeing what you’re looking for?
Review all our AP®, Honors, and Electives programs, including available formats, prices, and ISBNs
Contact Pearson
Our experts will guide you through available programs, eTextbooks, and printed materials.
With this form, you can request a sample, access instructor resources, or make a purchase.
AP® is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse, these programs.