Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
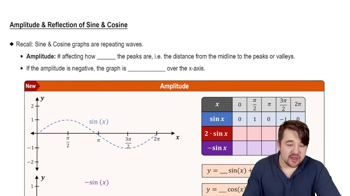
Amplitude
Amplitude refers to the maximum height of a wave from its central axis. In the context of trigonometric functions like cosine, it is determined by the coefficient in front of the cosine term. For the function y = 4 cos(2x − π), the amplitude is 4, indicating that the graph will oscillate between 4 and -4.
Recommended video:
Amplitude and Reflection of Sine and Cosine
Period
The period of a trigonometric function is the length of one complete cycle of the wave. It can be calculated using the formula 2π divided by the coefficient of x in the function. For y = 4 cos(2x − π), the period is 2π/2 = π, meaning the function will repeat its values every π units along the x-axis.
Recommended video:
Period of Sine and Cosine Functions
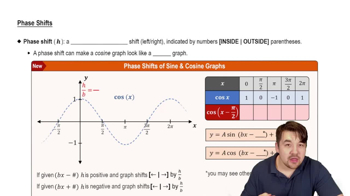
Phase Shift
Phase shift refers to the horizontal shift of the graph of a trigonometric function. It is determined by the constant added or subtracted from the x variable inside the function. In y = 4 cos(2x − π), the phase shift can be found by setting 2x - π = 0, leading to a shift of π/2 units to the right, which alters the starting point of the cosine wave.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution