Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions
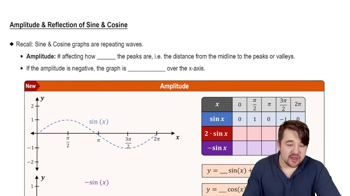
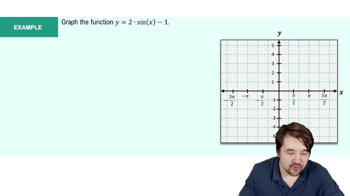
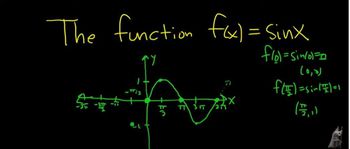
Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
Problem 77a
Textbook Question
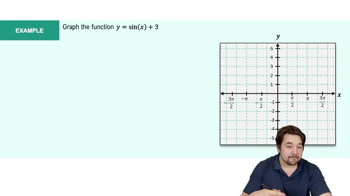
Textbook QuestionGraph each function. See Examples 6 – 8. _ ƒ(x) = 2√x + 1
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Square Root Function
The square root function, denoted as √x, is defined for non-negative values of x and produces the principal square root. It is a fundamental function in mathematics, characterized by its gradual increase and a domain of [0, ∞). Understanding its properties, such as its shape and behavior, is essential for graphing functions that involve square roots.
Recommended video:

Imaginary Roots with the Square Root Property
Transformation of Functions
Transformations of functions involve shifting, stretching, or compressing the graph of a function. In the given function ƒ(x) = 2√x + 1, the '2' indicates a vertical stretch by a factor of 2, while the '+1' represents a vertical shift upward by 1 unit. Recognizing these transformations helps in accurately graphing the function based on its parent function.
Recommended video:

Domain and Range of Function Transformations
Domain and Range
The domain of a function refers to the set of all possible input values (x-values), while the range is the set of all possible output values (y-values). For the function ƒ(x) = 2√x + 1, the domain is [0, ∞) since square roots are only defined for non-negative numbers, and the range is [1, ∞) due to the vertical shift. Understanding domain and range is crucial for graphing and interpreting functions.
Recommended video:

Domain and Range of Function Transformations

 5:53m
5:53mWatch next
Master Graph of Sine and Cosine Function with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice