Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Standard Position of an Angle
An angle is in standard position when its vertex is at the origin of a coordinate system and its initial side lies along the positive x-axis. The angle is measured from the initial side to the terminal side, with positive angles measured counterclockwise and negative angles measured clockwise. Understanding this positioning is crucial for visualizing and sketching angles accurately.
Recommended video:
Drawing Angles in Standard Position
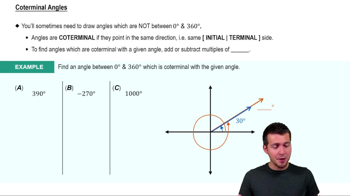
Coterminal Angles
Coterminal angles are angles that share the same terminal side when drawn in standard position, differing by full rotations of 360 degrees. To find coterminal angles, you can add or subtract multiples of 360 degrees from the given angle. For example, for a 90° angle, adding 360° gives 450°, while subtracting 360° results in -270°.
Recommended video:
Quadrants of the Coordinate Plane
The coordinate plane is divided into four quadrants, each defined by the signs of the x and y coordinates. Quadrant I has both coordinates positive, Quadrant II has a negative x and positive y, Quadrant III has both negative, and Quadrant IV has a positive x and negative y. Identifying the quadrant of an angle helps in understanding its position relative to the axes and is essential for determining the angle's properties.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 3:47m
3:47m