Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polar Coordinates
Polar coordinates represent points in a plane using a distance from a reference point (the origin) and an angle from a reference direction. In polar equations, 'r' denotes the radius (distance from the origin), and 'θ' represents the angle. Understanding how to interpret and manipulate these coordinates is essential for converting polar equations to rectangular form.
Recommended video:
Intro to Polar Coordinates
Rectangular Coordinates
Rectangular coordinates, or Cartesian coordinates, use the x and y axes to define a point in a plane. The conversion from polar to rectangular coordinates involves using the relationships x = r cos(θ) and y = r sin(θ). This transformation is crucial for analyzing the properties of the graph, such as slope and y-intercept, in a familiar coordinate system.
Recommended video:
Convert Points from Polar to Rectangular
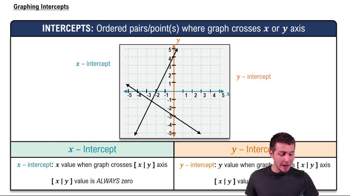
Slope and Y-Intercept
The slope of a line in a rectangular coordinate system indicates its steepness and direction, while the y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis. To find these values from a rectangular equation, one typically rearranges the equation into slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), where 'm' represents the slope and 'b' the y-intercept. This understanding is vital for interpreting the graph of the equation derived from the polar form.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 5:32m
5:32m