Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
10. Parametric Equations
Graphing Parametric Equations
Problem 8.33
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionGraph each plane curve defined by the parametric equations for t in [0, 2π] Then find a rectangular equation for the plane curve. See Example 3.
x = 2 + sin t , y = 1 + cos t
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
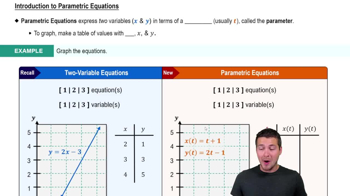
Parametric Equations
Parametric equations express the coordinates of points on a curve as functions of a variable, typically denoted as 't'. In this case, x and y are defined in terms of 't', allowing for the representation of curves that may not be easily described by a single equation. Understanding how to manipulate and graph these equations is essential for visualizing the curve they represent.
Recommended video:

Parameterizing Equations
Graphing Techniques
Graphing techniques involve plotting points on a coordinate system based on the values derived from the parametric equations. For the given equations, one would calculate x and y for various values of 't' within the specified range [0, 2π] to create a visual representation of the curve. Familiarity with graphing tools and software can enhance this process, making it easier to visualize complex curves.
Recommended video:
Graphing Intercepts
Rectangular Equation
A rectangular equation eliminates the parameter 't' to express the relationship between x and y directly. This is often achieved by solving one of the parametric equations for 't' and substituting it into the other. The resulting equation provides a more traditional representation of the curve, which can be useful for further analysis and understanding of its properties.
Recommended video:

Convert Equations from Rectangular to Polar

 4:47m
4:47mWatch next
Master Introduction to Parametric Equations with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learning