Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
0. Review of College Algebra
Basics of Graphing
Problem 1
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionCONCEPT PREVIEW Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence. The point (-1, 3) lies in quadrant ________ in the rectangular coordinate system.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
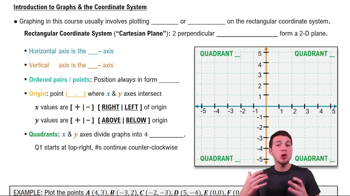
Quadrants in the Coordinate System
The rectangular coordinate system is divided into four quadrants based on the signs of the x and y coordinates. Quadrant I has positive x and y values, Quadrant II has negative x and positive y values, Quadrant III has negative x and y values, and Quadrant IV has positive x and negative y values. Understanding these quadrants is essential for determining the location of points in the plane.
Recommended video:

Intro to Polar Coordinates
Coordinate Points
A coordinate point is represented as an ordered pair (x, y), where 'x' indicates the horizontal position and 'y' indicates the vertical position on the coordinate plane. The first value corresponds to the x-coordinate, which determines the point's distance from the y-axis, while the second value corresponds to the y-coordinate, indicating its distance from the x-axis. This structure is fundamental for locating points in the coordinate system.
Recommended video:

Determining Different Coordinates for the Same Point
Sign of Coordinates
The sign of the coordinates (positive or negative) determines the quadrant in which a point lies. For example, a point with a negative x-coordinate and a positive y-coordinate, like (-1, 3), will be located in Quadrant II. Recognizing the significance of these signs is crucial for accurately identifying the position of points in the coordinate system.
Recommended video:

Intro to Polar Coordinates

 5:1m
5:1mWatch next
Master Introduction to Graphs & the Coordinate System with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learning