Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles40m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations
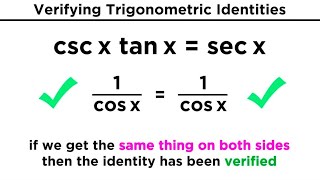
Introduction to Trigonometric Identities

Example 5
Callie Rethman
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Related Videos
Related Practice