Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
3. Unit Circle
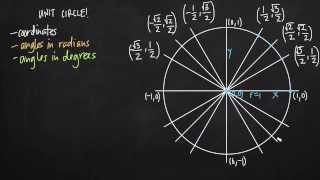
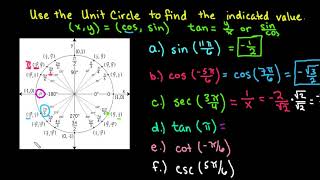
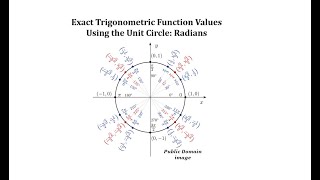
Defining the Unit Circle
Problem 3.21a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionUse the formula v = r ω to find the value of the missing variable.
r = 12 m , ω = 2π/3 radians per sec
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Angular Velocity (ω)
Angular velocity (ω) measures how quickly an object rotates around a central point, expressed in radians per second. It indicates the angle covered per unit of time, allowing us to understand the rotational speed of an object. In this question, ω is given as 2π/3 radians per second, which is essential for calculating linear velocity.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Vectors
Radius (r)
The radius (r) is the distance from the center of a circle to any point on its circumference. In the context of circular motion, the radius plays a crucial role in determining the linear velocity of an object moving along a circular path. Here, the radius is provided as 12 meters, which is necessary for applying the formula v = rω.
Recommended video:

Intro to Polar Coordinates Example 1
Linear Velocity (v)
Linear velocity (v) represents the speed of an object moving along a circular path and is calculated using the formula v = rω. This formula shows that linear velocity is directly proportional to both the radius and the angular velocity. By substituting the given values of r and ω into this formula, we can find the missing variable, which is the linear velocity.
Recommended video:

Categorizing Linear Equations

 6:11m
6:11mWatch next
Master Introduction to the Unit Circle with a bite sized video explanation from Callie Rethman
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice