Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions
Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
Problem 4.1a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionAn object in simple harmonic motion has position function s(t), in inches, from an equilibrium point, as follows, where t is time in seconds.
𝒮(t) = 5 cos 2t
What is the amplitude of this motion?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
Simple Harmonic Motion is a type of periodic motion where an object oscillates around an equilibrium position. The motion is characterized by a restoring force proportional to the displacement from the equilibrium, leading to sinusoidal functions in its position, velocity, and acceleration. In SHM, the position function can typically be expressed in terms of sine or cosine functions.
Recommended video:

Products of Complex Numbers in Polar Form
Amplitude
Amplitude is a key characteristic of oscillatory motion, representing the maximum displacement of an object from its equilibrium position. In the context of the position function s(t) = A cos(ωt), the amplitude A indicates how far the object moves from the center point during its motion. For the given function, the amplitude is the coefficient of the cosine term.
Recommended video:
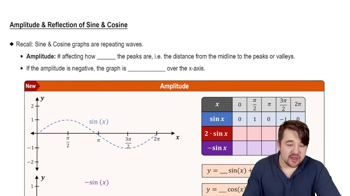
Amplitude and Reflection of Sine and Cosine
Cosine Function
The cosine function is a fundamental trigonometric function that describes the relationship between the angle and the adjacent side of a right triangle. In the context of SHM, the cosine function is used to model the position of an oscillating object over time. The general form s(t) = A cos(ωt) shows how the position varies with time, where A is the amplitude and ω is the angular frequency.
Recommended video:

Graph of Sine and Cosine Function

 5:53m
5:53mWatch next
Master Graph of Sine and Cosine Function with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice