Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
3. Unit Circle
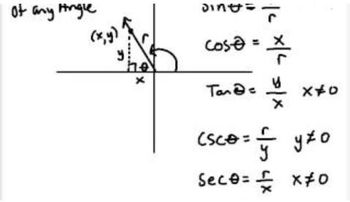
Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
Problem 77
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFind a formula for the area of each figure in terms of s.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle can be calculated using the formula A = 1/2 * base * height. However, when the lengths of the sides are known, Heron's formula can be used, which states that the area A is given by A = √(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)), where s is the semi-perimeter and a, b, c are the lengths of the sides.
Recommended video:
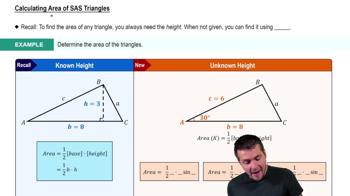
Calculating Area of SAS Triangles
Semi-Perimeter
The semi-perimeter of a triangle is defined as half of the perimeter. It is calculated as s = (a + b + c) / 2, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the triangle's sides. The semi-perimeter is a crucial component in Heron's formula for calculating the area of a triangle.
Recommended video:

Equations with Trigonometric Functions Example 3
Heron's Formula
Heron's formula provides a way to calculate the area of a triangle when the lengths of all three sides are known. It utilizes the semi-perimeter and is expressed as A = √(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)). This formula is particularly useful for triangles where height is not easily determined.
Recommended video:

Quadratic Formula

 6:34m
6:34mWatch next
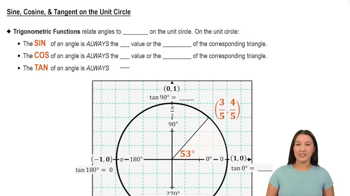
Master Sine, Cosine, & Tangent on the Unit Circle with a bite sized video explanation from Callie Rethman
Start learning