Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations
Introduction to Trigonometric Identities
Problem 5.86
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionVerify that each equation is an identity.
sin² x(1 + cot x) + cos² x(1 - tan x) + cot² x = csc² x
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric identities are equations that hold true for all values of the variable where both sides are defined. Common identities include the Pythagorean identities, reciprocal identities, and quotient identities. Understanding these identities is crucial for verifying equations and simplifying expressions in trigonometry.
Recommended video:

Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
Reciprocal Functions
Reciprocal functions in trigonometry relate the sine, cosine, and tangent functions to their reciprocals: cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot). For example, csc x = 1/sin x and cot x = 1/tan x. Recognizing these relationships helps in transforming and simplifying trigonometric expressions.
Recommended video:
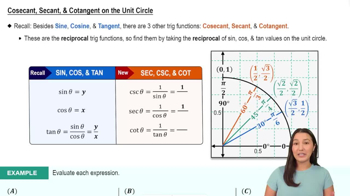
Secant, Cosecant, & Cotangent on the Unit Circle
Simplification Techniques
Simplification techniques involve manipulating trigonometric expressions using identities to make them easier to analyze or verify. This can include factoring, combining like terms, or substituting equivalent expressions. Mastery of these techniques is essential for proving that an equation is an identity.
Recommended video:

Example 6

 6:19m
6:19mWatch next
Master Even and Odd Identities with a bite sized video explanation from Callie Rethman
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice