Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions
Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
Problem 13b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 12–13, use a vertical shift to graph one period of the function. y = 2 cos 1/3 x − 2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
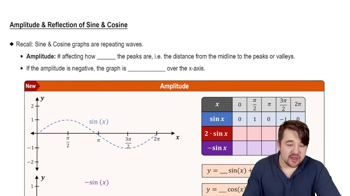
Cosine Function
The cosine function is a fundamental trigonometric function that describes the relationship between the angle and the adjacent side over the hypotenuse in a right triangle. It is periodic, with a standard period of 2π, meaning it repeats its values every 2π radians. The graph of the cosine function is a wave that oscillates between -1 and 1, and it is symmetric about the y-axis.
Recommended video:

Graph of Sine and Cosine Function
Vertical Shift
A vertical shift in a function occurs when a constant is added or subtracted from the function's output. In the given function, y = 2 cos(1/3 x) - 2, the '-2' indicates a downward shift of the entire cosine graph by 2 units. This transformation affects the midline of the graph, moving it from y=0 to y=-2, while the amplitude and period remain unchanged.
Recommended video:
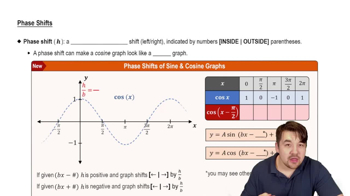
Phase Shifts
Amplitude and Period
The amplitude of a trigonometric function refers to the height of the wave from its midline to its maximum or minimum value. In the function y = 2 cos(1/3 x) - 2, the amplitude is 2, indicating the graph will reach a maximum of -2 + 2 = 0 and a minimum of -2 - 2 = -4. The period, determined by the coefficient of x, is calculated as 2π divided by the coefficient, resulting in a period of 6π for this function.
Recommended video:

Period of Sine and Cosine Functions

 5:53m
5:53mWatch next
Master Graph of Sine and Cosine Function with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice