Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Right Triangle Properties
A right triangle has one angle measuring 90 degrees, and the other two angles must sum to 90 degrees. This property allows for the use of trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, and tangent) to relate the angles and sides of the triangle. Understanding these relationships is crucial for solving for unknown angles and sides.
Recommended video:
Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric ratios are defined as the ratios of the lengths of the sides of a right triangle relative to its angles. For example, sine is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cosine is the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tangent is the opposite side to the adjacent side. These ratios are essential for calculating unknown sides or angles in a triangle.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Angle Measurement Conversions
Angles can be measured in degrees and minutes or in decimal degrees. When solving triangles, it is important to maintain consistency in the format of angle measurements. Converting between these formats may be necessary, especially when given angles in different forms, to ensure accurate calculations and results.
Recommended video:
Reference Angles on the Unit Circle
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution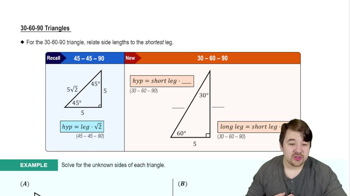



 4:18m
4:18m
