Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions
Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
Problem 4.9aLial - 12th Edition
Textbook Question
Match each function with its graph in choices A–I. (One choice will not be used.)
y = sin (x - π/4)
A. <IMAGE> B. <IMAGE> C. <IMAGE>
D. <IMAGE> E. <IMAGE> F. <IMAGE>
G. <IMAGE> H. <IMAGE> I. <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the basic shape and properties of the sine function, which has a periodic wave-like form oscillating between -1 and 1.
Understand the effect of the phase shift in the function y = sin(x - \frac{\pi}{4}). This represents a horizontal shift to the right by \frac{\pi}{4} units.
Look for a graph among the choices that shows a sine wave starting at a phase shift of -\frac{\pi}{4} on the x-axis. This means the wave, which usually starts at 0, should start at -\frac{\pi}{4}.
Check the amplitude and period of the sine function in the graph. The amplitude should be 1 (distance from the center line to the peak), and the period should be 2\pi, as there are no changes to these in the given function.
Eliminate any graph that does not start at -\frac{\pi}{4} or does not maintain the standard sine wave properties of amplitude 1 and period 2\pi.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sine Function Properties
The sine function, denoted as sin(x), is a periodic function that oscillates between -1 and 1. It has a fundamental period of 2π, meaning it repeats its values every 2π units. Understanding the basic shape and behavior of the sine wave is crucial for identifying its transformations, such as shifts and stretches.
Recommended video:

Graph of Sine and Cosine Function
Phase Shift
A phase shift occurs when the input of a function is altered by a constant, affecting the horizontal position of the graph. For the function y = sin(x - π/4), the phase shift is π/4 units to the right. This shift modifies the starting point of the sine wave, which is essential for matching the function to its corresponding graph.
Recommended video:
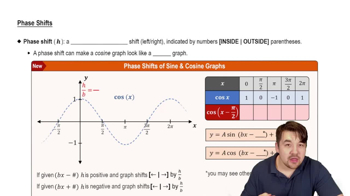
Phase Shifts
Graphical Representation of Functions
Graphical representation involves plotting the values of a function on a coordinate plane, allowing for visual analysis of its behavior. Recognizing key features such as amplitude, period, and phase shifts helps in accurately matching a function to its graph. Familiarity with how transformations affect the graph is vital for this task.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Relations and Functions

 5:53m
5:53mWatch next
Master Graph of Sine and Cosine Function with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
In Exercises 1–6, determine the amplitude of each function. Then graph the function and y = sin x in the same rectangular coordinate system for 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π.
y = 4 sin x
376
views
