Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
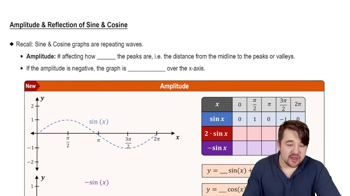
Amplitude
Amplitude refers to the maximum distance a wave reaches from its central axis or equilibrium position. In the context of trigonometric functions like cosine, the amplitude is determined by the coefficient in front of the cosine term. For the function y = cos(x + π/2), the amplitude is 1, indicating that the graph oscillates between 1 and -1.
Recommended video:
Amplitude and Reflection of Sine and Cosine
Period
The period of a trigonometric function is the length of one complete cycle of the wave. For the cosine function, the standard period is 2π. In the function y = cos(x + π/2), there are no coefficients affecting the x variable, so the period remains 2π, meaning the function will repeat its values every 2π units along the x-axis.
Recommended video:
Period of Sine and Cosine Functions
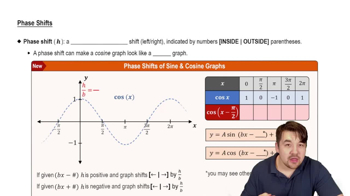
Phase Shift
Phase shift refers to the horizontal displacement of a trigonometric function from its standard position. It is determined by the value added or subtracted from the x variable inside the function. In y = cos(x + π/2), the phase shift is -π/2, indicating that the graph is shifted π/2 units to the left along the x-axis.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution