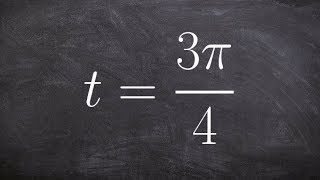Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
3. Unit Circle
Defining the Unit Circle
Problem 16
Textbook Question
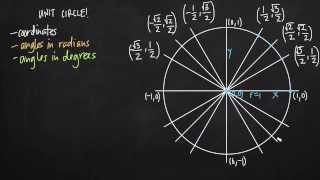
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 5–18, the unit circle has been divided into twelve equal arcs, corresponding to t-values of
0, 𝜋, 𝜋, 𝜋, 2𝜋, 5𝜋, 𝜋, 7𝜋, 4𝜋, 3𝜋, 5𝜋, 11𝜋, and 2𝜋.
6 3 2 3 6 6 3 2 3 6
Use the (x,y) coordinates in the figure to find the value of each trigonometric function at the indicated real number, t, or state that the expression is undefined.

In Exercises 11–18, continue to refer to the figure at the bottom of the previous page.
cos 3𝜋/2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Unit Circle
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It is used to define trigonometric functions for all real numbers. The coordinates of points on the unit circle correspond to the cosine and sine values of angles measured in radians, allowing for easy calculation of these functions.
Recommended video:

Introduction to the Unit Circle
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. On the unit circle, the cosine of an angle corresponds to the x-coordinate, while the sine corresponds to the y-coordinate of the point on the circle. Understanding these functions is essential for solving problems involving angles and their relationships.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Radians
Radians are a unit of angular measure used in mathematics, where one radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. The unit circle divides the circle into radians, making it easier to work with angles in trigonometric functions. For example, 3π/2 radians corresponds to 270 degrees, which is a key angle in trigonometry.
Recommended video:

Converting between Degrees & Radians

 6:11m
6:11mWatch next
Master Introduction to the Unit Circle with a bite sized video explanation from Callie Rethman
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice