Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles
Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles
Problem 31c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFind the values of the six trigonometric functions for an angle in standard position having each given point on its terminal side. Rationalize denominators when applicable. (6√3 , ―6)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trigonometric Functions
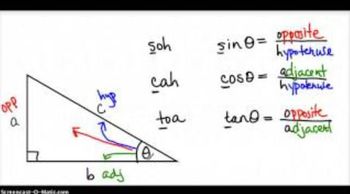
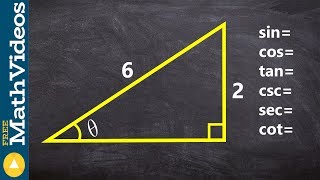
The six trigonometric functions—sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent—are fundamental in relating angles to the ratios of sides in a right triangle. For a point (x, y) on the terminal side of an angle in standard position, these functions can be defined as: sine = y/r, cosine = x/r, and tangent = y/x, where r is the distance from the origin to the point, calculated as r = √(x² + y²).
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Standard Position of an Angle
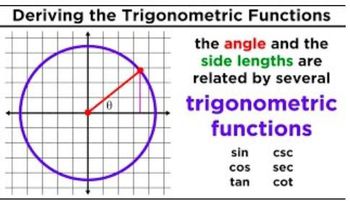
An angle is said to be in standard position when its vertex is at the origin of a coordinate system and its initial side lies along the positive x-axis. The terminal side of the angle is determined by rotating the initial side counterclockwise. The coordinates of any point on the terminal side can be used to find the values of the trigonometric functions associated with that angle.
Recommended video:

Drawing Angles in Standard Position
Rationalizing Denominators
Rationalizing the denominator is a mathematical process used to eliminate any radical expressions from the denominator of a fraction. This is often done by multiplying the numerator and denominator by a suitable value that will result in a rational number in the denominator. In trigonometry, this is particularly important when dealing with trigonometric function values that involve square roots, ensuring that the final answers are presented in a standard form.
Recommended video:

Rationalizing Denominators

 6:4m
6:4mWatch next
Master Introduction to Trigonometric Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice