Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
3. Unit Circle
Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
Problem 7b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe unit circle has been divided into twelve equal arcs, corresponding to t-values of
0, 𝜋/6, 𝜋/3, 𝜋/2, 2𝜋/3, 5𝜋/6, 𝜋, 7𝜋/6, 4𝜋/3, 3𝜋/2, 5𝜋/3, 11𝜋/6, and 2𝜋
Use the (x,y) coordinates in the figure to find the value of each trigonometric function at the indicated real number, t, or state that the expression is undefined.
<IMAGE>
cos 5𝜋/6
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Unit Circle
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It is fundamental in trigonometry as it provides a geometric representation of the sine and cosine functions. Each point on the unit circle corresponds to an angle measured in radians, where the x-coordinate represents the cosine value and the y-coordinate represents the sine value of that angle.
Recommended video:

Introduction to the Unit Circle
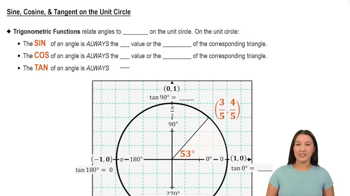
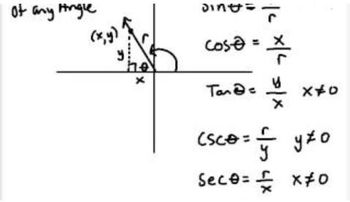
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, including sine, cosine, and tangent, relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. On the unit circle, the cosine of an angle is the x-coordinate of the corresponding point, while the sine is the y-coordinate. Understanding these functions is essential for evaluating trigonometric expressions at specific angles, such as 5π/6.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Reference Angles
Reference angles are the acute angles formed by the terminal side of an angle and the x-axis. They help in determining the values of trigonometric functions for angles in different quadrants. For example, the reference angle for 5π/6 is π/6, which allows us to find the cosine value by considering the sign based on the quadrant in which the angle lies.
Recommended video:

Reference Angles on the Unit Circle

 6:34m
6:34mWatch next
Master Sine, Cosine, & Tangent on the Unit Circle with a bite sized video explanation from Callie Rethman
Start learning