Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions
Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
Problem 21b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionGraph each function. See Examples 1 and 2. g(x) = ½ x²
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, typically expressed in the form g(x) = ax² + bx + c. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola, which can open upwards or downwards depending on the sign of the coefficient 'a'. In this case, g(x) = ½ x² represents a parabola that opens upwards, with its vertex at the origin (0,0).
Recommended video:

Quadratic Formula
Graphing Techniques
Graphing a function involves plotting points on a coordinate plane to visualize its behavior. For quadratic functions, key points include the vertex, axis of symmetry, and intercepts. The vertex can be found using the formula x = -b/(2a), and the y-intercept occurs when x = 0. Understanding these points helps in accurately sketching the graph.
Recommended video:
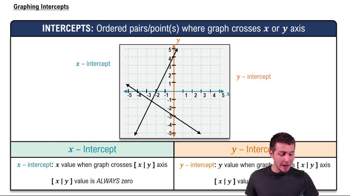
Graphing Intercepts
Transformation of Functions
Transformations involve shifting, stretching, or reflecting the graph of a function. For the function g(x) = ½ x², the coefficient ½ indicates a vertical compression, making the parabola wider than the standard x² graph. Recognizing how changes in coefficients affect the shape and position of the graph is essential for accurate representation.
Recommended video:

Domain and Range of Function Transformations

 5:53m
5:53mWatch next
Master Graph of Sine and Cosine Function with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice