Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
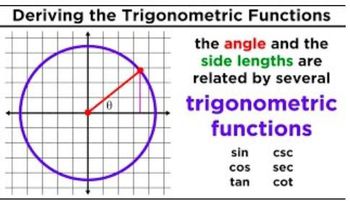
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles
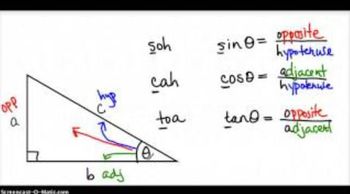
Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles
Problem 103
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionConcept Check Suppose that ―90° < θ < 90° . Find the sign of each function value. cos(θ―180°)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Understanding Angle Measures
In trigonometry, angles can be measured in degrees or radians. The question specifies that θ is between -90° and 90°, which indicates that θ is in the first or fourth quadrant. This range is crucial for determining the signs of trigonometric functions, as the sign of a function can vary depending on the quadrant in which the angle lies.
Recommended video:

Reference Angles on the Unit Circle
Cosine Function and Its Properties
The cosine function, denoted as cos(θ), represents the x-coordinate of a point on the unit circle corresponding to the angle θ. The cosine function is positive in the first quadrant and negative in the second quadrant. Understanding how the cosine function behaves with respect to angle transformations, such as cos(θ - 180°), is essential for determining its sign.
Recommended video:

Graph of Sine and Cosine Function
Angle Transformation
Angle transformation involves adjusting an angle by adding or subtracting a specific value. In this case, cos(θ - 180°) indicates a shift of the angle θ by 180°, which effectively reflects the angle across the origin on the unit circle. This transformation changes the sign of the cosine value, making it important to analyze how this affects the function's output based on the original angle θ.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Transformations

 6:4m
6:4mWatch next
Master Introduction to Trigonometric Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice