Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
3. Unit Circle
Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
Problem 3
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionCONCEPT PREVIEW Match each trigonometric function in Column I with its value in Column II. Choices may be used once, more than once, or not at all. I II 1. A. √3 2. B. 1 3. tan 45° C. ½ 4. D. √3 5. 2 6. E. 2√3 3 F. √3 3 G. 2 H. √2 2 I. √2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
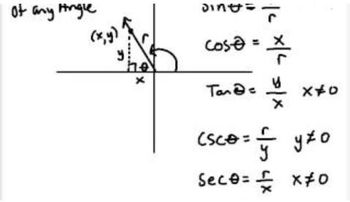
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. The primary functions include sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan), which are defined for a right triangle as the ratios of the lengths of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and opposite side to the adjacent side, respectively. Understanding these functions is essential for solving problems involving angles and side lengths.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
Special Angles
Certain angles, such as 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°, have known values for their trigonometric functions, often referred to as special angles. For example, tan 45° equals 1, and sin 30° equals ½. Familiarity with these values allows for quick calculations and is crucial for matching functions to their corresponding values in problems like the one presented.
Recommended video:

45-45-90 Triangles
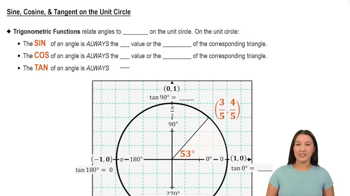
Unit Circle
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of one centered at the origin of a coordinate plane. It provides a geometric interpretation of trigonometric functions, where the x-coordinate represents the cosine and the y-coordinate represents the sine of an angle. Understanding the unit circle helps in determining the values of trigonometric functions for various angles, facilitating the matching process in the given question.
Recommended video:

Introduction to the Unit Circle

 6:34m
6:34mWatch next
Master Sine, Cosine, & Tangent on the Unit Circle with a bite sized video explanation from Callie Rethman
Start learning