Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
7. Non-Right Triangles
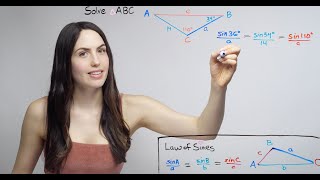
Law of Sines
Problem 7.1b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWhich one of the following sets of data does not determine a unique triangle?
a. A = 50°, b = 21, a = 19
b. A = 45°, b = 10, a = 12
c. A = 130°, b = 4, a = 7
d. A = 30°, b = 8, a = 4
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Triangle Congruence Criteria
Triangle congruence criteria are rules that determine when two triangles are congruent, meaning they have the same size and shape. The most common criteria include Side-Angle-Side (SAS), Angle-Side-Angle (ASA), and Side-Side-Side (SSS). Understanding these criteria helps in identifying whether a given set of measurements can form a unique triangle.
Recommended video:
30-60-90 Triangles
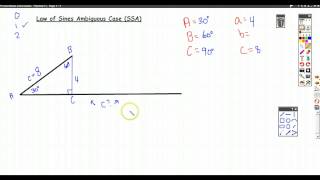
Ambiguous Case of the Law of Sines
The ambiguous case occurs when using the Law of Sines to solve for a triangle with two sides and a non-included angle (SSA). This situation can lead to zero, one, or two possible triangles, depending on the specific values of the sides and angle. Recognizing this case is crucial for determining whether a unique triangle can be formed.
Recommended video:

Solving SSA Triangles ("Ambiguous" Case)
Sum of Angles in a Triangle
The sum of the interior angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees. This fundamental property is essential for verifying the validity of angle measures provided in triangle problems. If the angles do not sum to 180 degrees, the given data cannot form a triangle, which is a key consideration in the question.
Recommended video:
Sum and Difference of Tangent

 4:27m
4:27mWatch next
Master Intro to Law of Sines with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice