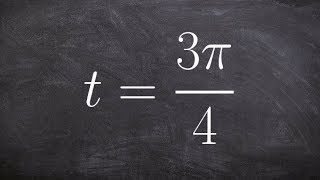Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
3. Unit Circle
Defining the Unit Circle
Problem 3.63
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFind the approximate value of s, to four decimal places, in the interval [0, π/2] that makes each statement true.
sin s = 0.9918
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sine Function
The sine function, denoted as sin, is a fundamental trigonometric function that relates the angle of a right triangle to the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. It is periodic and oscillates between -1 and 1. In the context of the unit circle, sin s represents the y-coordinate of a point on the circle corresponding to the angle s.
Recommended video:

Graph of Sine and Cosine Function
Inverse Sine Function
The inverse sine function, or arcsin, is used to determine the angle whose sine is a given value. It is denoted as sin⁻¹(x) and is defined for values in the range [-1, 1]. The output of arcsin is restricted to the interval [-π/2, π/2], but when considering the sine function's periodicity, we can find angles in other intervals, such as [0, π/2].
Recommended video:

Inverse Sine
Interval Notation
Interval notation is a mathematical notation used to represent a range of values. In this case, the interval [0, π/2] indicates that we are looking for solutions within the closed range from 0 to π/2, inclusive. This is important for determining the valid angles for which the sine function can yield the specified value, ensuring that the solution adheres to the constraints of the problem.
Recommended video:

i & j Notation

 6:11m
6:11mWatch next
Master Introduction to the Unit Circle with a bite sized video explanation from Callie Rethman
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice