Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions
Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
Problem 4.44b
Textbook Question
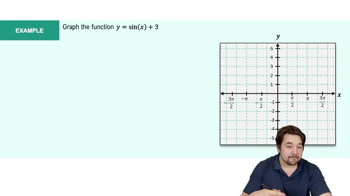
Textbook QuestionDetermine the simplest form of an equation for each graph. Choose b > 0, and include no phase shifts.
<IMAGE>
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
0m:0sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, are fundamental in describing periodic phenomena. Each function has a specific range and period, which determines how the function behaves over its domain. Understanding these functions is crucial for analyzing graphs, as they dictate the shape and characteristics of the waveforms represented.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
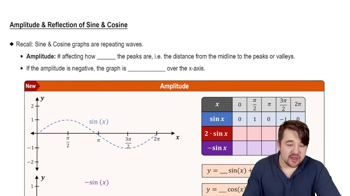
Amplitude and Period
Amplitude refers to the height of the wave from its midline to its peak, while the period is the distance over which the wave completes one full cycle. In trigonometric equations, the amplitude is influenced by a coefficient in front of the function, and the period is determined by the coefficient of the variable inside the function. Recognizing these properties helps in constructing the correct equation for a given graph.
Recommended video:

Period of Sine and Cosine Functions
Vertical Shift
A vertical shift occurs when a trigonometric function is moved up or down on the graph, affecting its midline. This shift is represented by adding or subtracting a constant to the function. In the context of the question, understanding vertical shifts is essential for accurately determining the simplest form of the equation, especially when no phase shifts are involved.
Recommended video:
Phase Shifts

 5:53m
5:53mWatch next
Master Graph of Sine and Cosine Function with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice