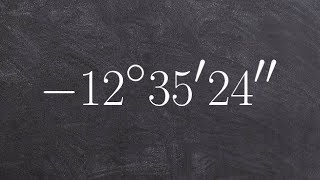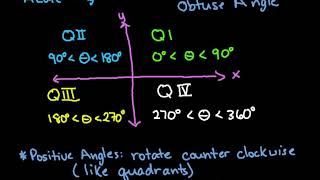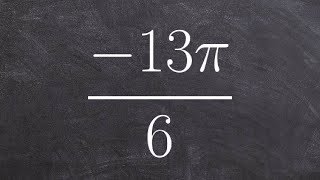Table of contents
- 0. Review of College Algebra4h 43m
- 1. Measuring Angles39m
- 2. Trigonometric Functions on Right Triangles2h 5m
- 3. Unit Circle1h 19m
- 4. Graphing Trigonometric Functions1h 19m
- 5. Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Basic Trigonometric Equations1h 41m
- 6. Trigonometric Identities and More Equations2h 34m
- 7. Non-Right Triangles1h 38m
- 8. Vectors2h 25m
- 9. Polar Equations2h 5m
- 10. Parametric Equations1h 6m
- 11. Graphing Complex Numbers1h 7m
1. Measuring Angles
Angles in Standard Position
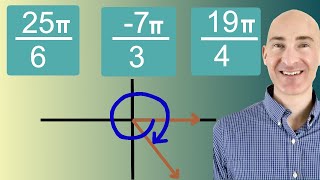
Problem 81b
Textbook Question
Textbook Question(Modeling) Speed of Light When a light ray travels from one medium, such as air, to another medium, such as water or glass, the speed of the light changes, and the light ray is bent, or refracted, at the boundary between the two media. (This is why objects under water appear to be in a different position from where they really are.) It can be shown in physics that these changes are related by Snell's law c₁ = sin θ₁ , c₂ sin θ₂ where c₁ is the speed of light in the first medium, c₂ is the speed of light in the second medium, and θ₁ and θ₂ are the angles shown in the figure. In Exercises 81 and 82, assume that c₁ = 3 x 10⁸ m per sec. Find the speed of light in the second medium for each of the following. a. θ₁ = 46°, θ₂ = 31° b. θ₁ = 39°, θ₂ = 28°
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Video transcript

 5:50m
5:50mWatch next
Master Drawing Angles in Standard Position with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice