My course
What would you like help with today?
Get world-class educational content with clear, step-by-step explanations all in one place
Start Learning and Practicing Statistics with Patrick - Your Online Course Tutor!
Jump on your first topic
- Concept Video2:13Introduction to Statistics Channel1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data / Intro to Stats
- Concept05:53Parameters vs. Statistics1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data / Intro to Stats
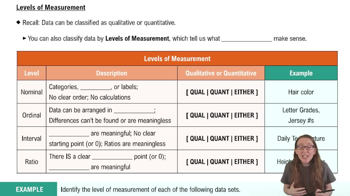
- Practice problem
You collect the test scores of every other student in a class. Is this data set a population or sample?
1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data / Intro to Stats
Most popular topics of the week
These are the topics other students have been focusing on.