Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
6. Learning
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
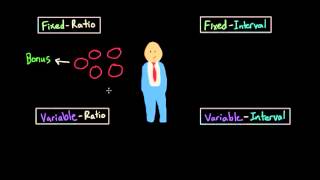
Tamar just cannot seem to get away from the slot machines. She has no idea how many times she has to pull the levers to win money, but she is aware that at some point, she is likely to win. What schedule of reinforcement is being used in this example?
A
Fixed interval
B
Fixed ratio
C
Variable interval
D
Variable ratio
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of reinforcement schedules in operant conditioning, which are rules that dictate how and when a response will be followed by a reinforcer.
Identify the four main types of reinforcement schedules: fixed interval, fixed ratio, variable interval, and variable ratio.
Recognize that a fixed interval schedule provides reinforcement after a set period of time, while a fixed ratio schedule provides reinforcement after a set number of responses.
Understand that a variable interval schedule provides reinforcement at unpredictable time intervals, whereas a variable ratio schedule provides reinforcement after an unpredictable number of responses.
Apply this understanding to the scenario: Tamar does not know how many times she needs to pull the lever to win, indicating that the reinforcement (winning) is based on an unpredictable number of responses, characteristic of a variable ratio schedule.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)