Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
6. Learning
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Marco's mom gives him a treat every night after dinner when he picks up his plate and places it in the dishwasher. Marco's mom uses
A
partial reinforcement.
B
continuous reinforcement.
C
a variable schedule of reinforcement.
D
negative reinforcement.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
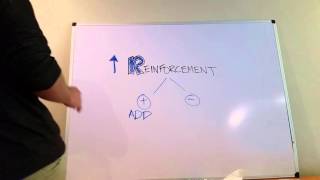
Understand the concept of reinforcement: Reinforcement is a fundamental concept in behavioral psychology that involves strengthening a behavior by providing a consequence that is rewarding.
Differentiate between types of reinforcement: Continuous reinforcement involves providing a reward every time a desired behavior occurs, while partial reinforcement involves providing rewards only some of the time.
Identify the reinforcement schedule in the scenario: Marco receives a treat every time he performs the desired behavior (placing his plate in the dishwasher), which aligns with continuous reinforcement.
Clarify the incorrect options: A variable schedule of reinforcement involves rewards given at unpredictable times, and negative reinforcement involves removing an unpleasant stimulus to increase a behavior.
Conclude by matching the scenario to the correct type of reinforcement: Since Marco receives a treat every time he performs the behavior, it is an example of continuous reinforcement.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)