Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
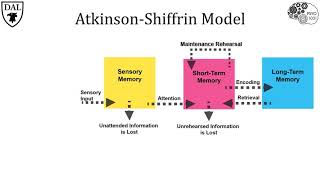
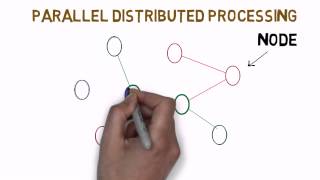
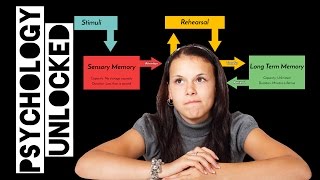
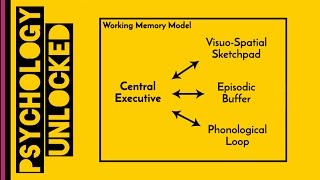
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
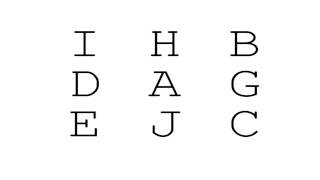
In spite of the loud music and many conversations at the party, Sarika was able to hear her friend say her name. Sarika's ability to hear her name regardless of the background noise is an example of
A
iconic memory.
B
selective attention.
C
procedural memory.
D
maintenance rehearsal.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of selective attention: It is the process by which a person focuses on one particular stimulus while ignoring others. This is crucial in environments with multiple stimuli, such as a noisy party.
Consider the scenario: Sarika is at a party with loud music and many conversations, which creates a challenging auditory environment.
Identify the key detail: Sarika hears her friend say her name despite the background noise. This indicates that her attention is drawn specifically to her name.
Relate this to selective attention: The ability to focus on a specific stimulus (her name) while filtering out other stimuli (background noise) is a classic example of selective attention.
Conclude that Sarika's experience aligns with the concept of selective attention, as it demonstrates her ability to prioritize certain auditory information over others in a complex environment.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)