Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
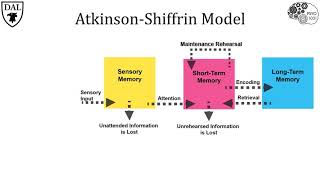
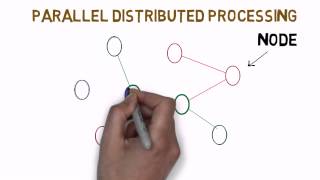
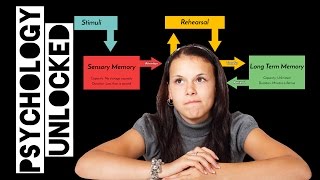
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Short-term memory tends to be encoded primarily in
A
visual form.
B
a 'sketchpad.'
C
auditory form.
D
working memory.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of short-term memory: Short-term memory is a part of the memory system where small amounts of information can be kept for a short period of time. It is crucial for tasks such as reasoning, learning, and comprehension.
Identify the typical encoding forms of short-term memory: Short-term memory can be encoded in various forms, including visual, auditory, and semantic. However, it is most commonly encoded in auditory form.
Clarify the role of auditory encoding: Auditory encoding involves the processing of information through sound. This is why people often remember phone numbers or lists by repeating them out loud.
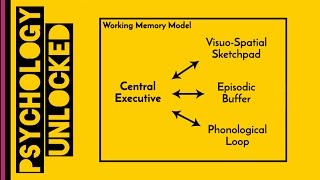
Differentiate between short-term memory and working memory: Working memory is a more complex system that involves the manipulation and processing of information held in short-term memory. It is often described as a 'sketchpad' for the mind.
Conclude with the correct answer: Given the options, the correct answer is that short-term memory tends to be encoded primarily in auditory form, not visual form or as a 'sketchpad.'

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)