Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
6. Learning
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
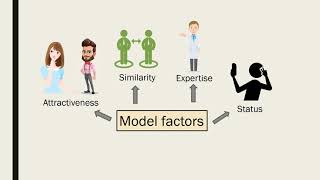
According to Bandura, to learn anything through observation, the learner must first
A
get a good night's sleep.
B
repeat everything that is said during the process.
C
pay attention.
D
be motivated.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context of observational learning as proposed by Albert Bandura, which involves learning by watching others.
Identify the key components of observational learning according to Bandura: attention, retention, reproduction, and motivation.
Focus on the first component, 'attention,' which is crucial for learning through observation. Without paying attention, the learner cannot effectively observe and learn from the model.
Consider why attention is necessary: it allows the learner to focus on the important aspects of the behavior being modeled, ensuring that the information is accurately perceived and processed.
Reflect on how attention can be influenced by various factors such as the characteristics of the model, the complexity of the behavior, and the learner's own interests and cognitive abilities.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)