Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
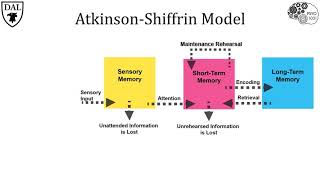
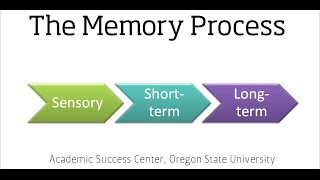
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Amanda was reading through her course text, but found she could not remember anything that she read. She realized that although she was seeing the words, she was not processing the information. The information-processing memory system being used by Amanda was _____ memory.
A
short-term
B
echoic
C
sensory
D
working
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the concept of the information-processing memory system, which includes sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
Sensory memory is the initial stage that holds all incoming information for a very short period of time. It acts as a buffer for stimuli received through the senses.
Consider the characteristics of sensory memory: it is brief and pre-attentive, meaning it processes information before we consciously focus on it.
In Amanda's case, she is seeing the words but not processing them, indicating that the information is not moving beyond the sensory memory stage.
Conclude that Amanda is using sensory memory, as it involves the initial perception of stimuli without deeper processing or retention.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)