Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
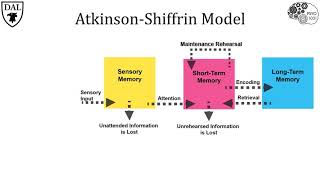
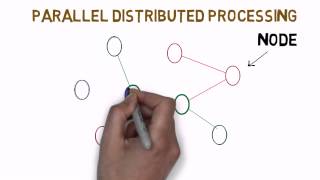
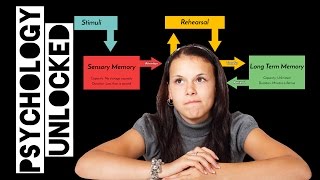
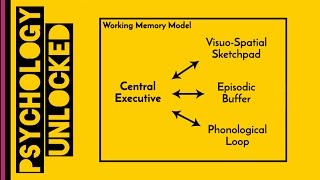
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
If a test measures what it is supposed to measure, that test has
A
reliability.
B
validity.
C
objectivity.
D
standardization.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of 'validity' in psychological testing. Validity refers to the degree to which a test accurately measures what it is intended to measure.
Differentiate between 'validity' and 'reliability'. Reliability refers to the consistency of a test's results over time, while validity is about the accuracy of what the test measures.
Consider the context of the question: it asks about a test measuring what it is supposed to measure, which directly relates to the concept of validity.
Review the definitions of the other options: 'objectivity' refers to the unbiased nature of a test, and 'standardization' refers to the uniform procedures used in administering and scoring a test.
Conclude that the correct term for a test that measures what it is supposed to measure is 'validity', as it aligns with the definition provided in the context of psychological testing.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)