Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
6. Learning
Classical Conditioning
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
After passing his chemistry exam, Tito was told by his parents that he would be able to have access to the family car for a week. Tito's parents are using
A
behavior modification.
B
shaping
C
higher-order conditioning.
D
positive reinforcement.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the key components of the scenario: Tito passed his chemistry exam, and as a result, his parents allowed him access to the family car for a week.
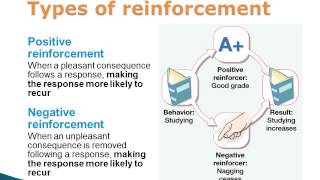
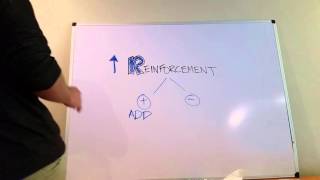
Understand the concept of positive reinforcement: It involves adding a rewarding stimulus after a desired behavior is performed, which increases the likelihood of the behavior being repeated.
Analyze the scenario: Tito's behavior (passing the exam) is followed by a positive consequence (access to the car), which is intended to encourage him to continue performing well in his studies.
Differentiate between the options: Behavior modification is a broad term that includes various techniques, shaping involves reinforcing successive approximations of a target behavior, and higher-order conditioning involves pairing a new neutral stimulus with a conditioned stimulus.
Conclude that the scenario is an example of positive reinforcement, as the reward (car access) is contingent upon the desired behavior (passing the exam), thereby reinforcing it.

 3:29m
3:29mWatch next
Master Introduction to Classical Conditioning with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

















![Visual Illusions - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/7GJJXLiN4Ug/mqdefault.jpg)


























![Classical Conditioning [cc]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/cP5lCleK-PM/mqdefault.jpg)












































































































![3.22. Tardive Dystonia Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation - Dystonias [Spring Video Atlas]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ayPFIpXhoWY/mqdefault.jpg)