Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
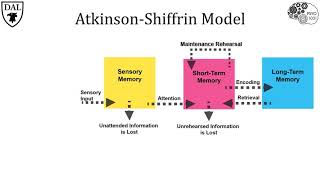
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Marcos and his friends enjoy watching football together on Sundays. After some of the games are over, Marcos tells his friends that he knew all along who would win the game. His belief that he could predict the outcome of some of the games without having been told the winners in advance is an example of
A
encoding specificity.
B
the primacy effect.
C
the misinformation effect.
D
hindsight bias.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the concept of hindsight bias. Hindsight bias is the tendency to believe, after an event has occurred, that one would have predicted or expected the outcome. It is often referred to as the 'I-knew-it-all-along' phenomenon.
Consider the scenario: Marcos claims he knew the outcome of the football games after they have ended. This is a classic example of hindsight bias, where he believes he could predict the results despite not having prior knowledge.
Differentiate hindsight bias from other cognitive biases mentioned: encoding specificity, primacy effect, and misinformation effect. Encoding specificity refers to the improved recall of information when the context present at encoding and retrieval are the same. The primacy effect is the tendency to remember the first items in a list better than those in the middle. The misinformation effect involves incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event.
Reflect on how hindsight bias can affect decision-making and judgment. It can lead individuals to overestimate their ability to predict events, potentially impacting their confidence and future predictions.
To further understand hindsight bias, consider how it might influence other areas of life, such as investing, relationships, or career decisions, where individuals might believe they could have foreseen outcomes after they have occurred.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)