Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
7. Memory
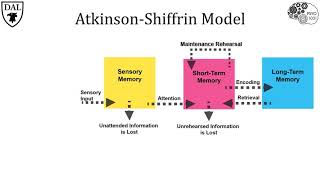
Information Processing Model
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Juana was certain that the man she saw in the police photograph was the man who stole her purse. Later, another man confessed to the crime. This is an example of
A
decay.
B
retrograde amnesia.
C
a false positive.
D
repression.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context: Juana identified a man in a police photograph as the thief, but another man later confessed to the crime.
Identify the psychological concept: This situation involves a memory error where Juana incorrectly identified someone as the perpetrator.
Consider the options: Decay refers to the fading of memory over time, retrograde amnesia involves loss of past memories, and repression is the unconscious blocking of distressing memories.
Focus on 'false positive': In psychology, a false positive occurs when a person incorrectly identifies or recalls something that did not happen or is not true.
Conclude that Juana's situation is an example of a false positive, as she mistakenly identified the wrong person as the thief.

 1:49m
1:49mWatch next
Master Information Processing Model with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice











































![Retrieving Memories [AP Psychology Unit 5 Topic 4] (5.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/2QC_4xuQyHA/mqdefault.jpg)












































![The Girl With The Three-Minute Memory (Amnesia Documentary) | Real Stories [4k]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZeiMhUlipTk/mqdefault.jpg)