Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
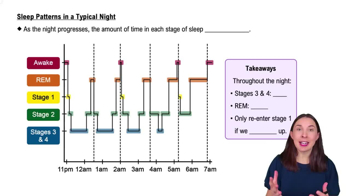
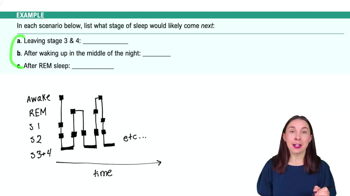
5. Consciousness and Sleep
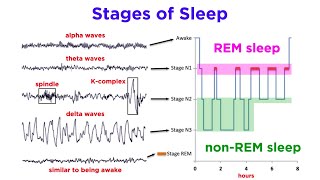
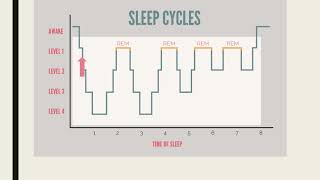
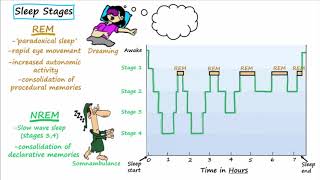
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Marion takes 20 minutes daily to sit by herself and meditate. A fully meditative state is a form of
A
waking consciousness.
B
altered state.
C
non-REM sleep.
D
convergent thinking.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of 'altered state of consciousness': This refers to any mental state that is significantly different from a normal waking state, such as meditation, hypnosis, or drug-induced states.
Recognize that meditation is a practice that can lead to an altered state of consciousness, where the mind is more focused and relaxed, often leading to changes in perception and awareness.
Differentiate between 'altered state' and 'non-REM sleep': Non-REM sleep is a natural state of rest that involves different brain activity patterns compared to waking consciousness, but it is not typically associated with meditation.
Consider 'convergent thinking': This is a cognitive process used to find a single, correct solution to a problem, which is not directly related to meditation or altered states of consciousness.
Conclude that the practice of meditation, as described in the problem, is most closely associated with an 'altered state of consciousness' due to its ability to change perception and awareness during the practice.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)