Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
5. Consciousness and Sleep
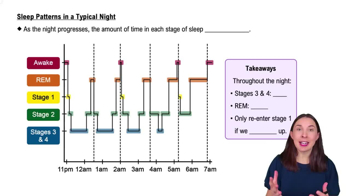
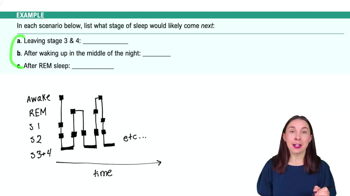
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Aristide believes that people who think they are hypnotized are not actually hypnotized at all. In fact, they are simply acting out everything that they are being told to do by the hypnotist. Aristide's way of thinking is similar to which of the following theories?
A
Freudian theory of hypnosis
B
Social-cognitive theory of hypnosis
C
Dissociative theory of hypnosis
D
Theory of hypnotic confusion
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the context of the problem: Aristide's belief is that people under hypnosis are not genuinely hypnotized but are instead acting out the suggestions given to them.
Identify the key elements of Aristide's belief: it focuses on the idea that individuals are consciously aware and are performing actions based on suggestions, rather than being in an altered state of consciousness.
Review the theories of hypnosis: Freudian theory, Social-cognitive theory, Dissociative theory, and Theory of hypnotic confusion.
Analyze the Social-cognitive theory of hypnosis: This theory suggests that hypnosis is not an altered state of consciousness but rather a form of social role-playing where individuals act according to the expectations set by the hypnotist.
Compare Aristide's belief with the Social-cognitive theory: Both suggest that the behavior of hypnotized individuals is a result of social influence and role-playing, aligning Aristide's belief with the Social-cognitive theory of hypnosis.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)