Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
3. Biological Psychology
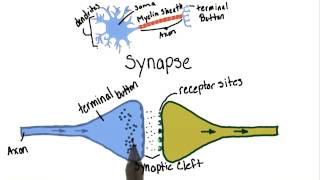
Communication in the Nervous System
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
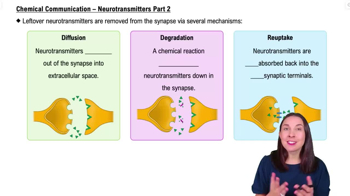
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that prevent the reuptake of serotonin. Based on this, which of the following statements is true regarding SSRIs?
A
SSRIs stop neurotransmitters from drifting out of the synapse.
B
SSRIs close the receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
C
SSRIs decrease the amount of time that serotonin is in the synapse.
D
SSRIs increase the amount of time that serotonin is in the synapse.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
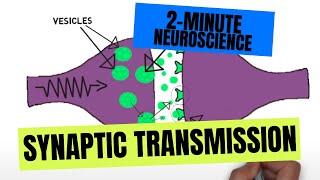
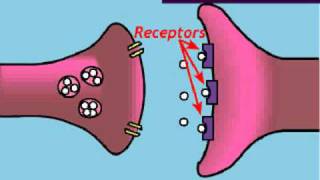
Understand the role of serotonin in the brain: Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in mood regulation, among other functions. It is released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft, where it can bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Learn about the reuptake process: Normally, after serotonin has been released into the synaptic cleft and has had the opportunity to bind to receptors, it is reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron in a process called reuptake. This process helps regulate the levels of serotonin in the synapse.
Explore the function of SSRIs: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are medications that block the reuptake of serotonin into the presynaptic neuron. By preventing reuptake, SSRIs increase the concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft.
Analyze the effect of SSRIs on serotonin levels: By inhibiting the reuptake process, SSRIs allow serotonin to remain in the synaptic cleft for a longer period of time, increasing the likelihood that it will bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Conclude the true statement about SSRIs: Given the mechanism of action of SSRIs, the correct statement is that SSRIs increase the amount of time that serotonin is in the synapse, enhancing its effects on mood and other functions.

 1:20m
1:20mWatch next
Master Electrochemical Communication with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice