Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
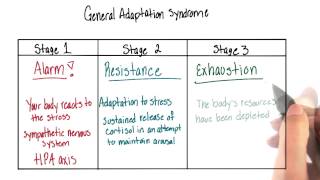
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
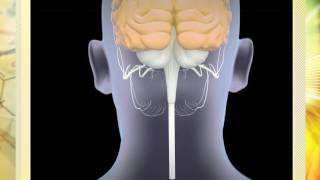
5. Consciousness and Sleep
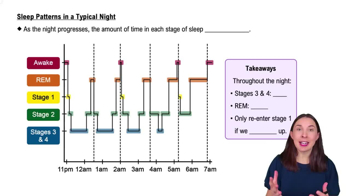
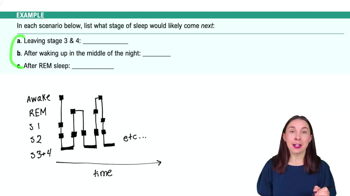
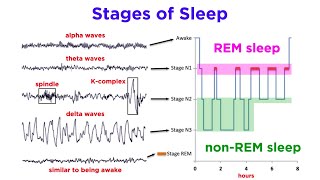
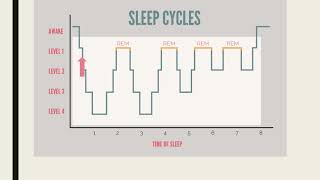
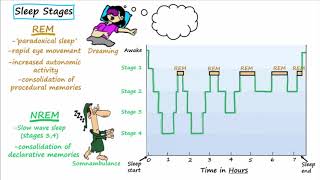
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
According to the _____, a dream is merely another kind of thinking that occurs when people sleep.
A
activation-synthesis hypothesis
B
psychoanalytic model
C
restorative theory
D
adaptive theory
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the key concept being asked about in the problem, which is related to the interpretation of dreams.
Review the provided options: activation-synthesis hypothesis, psychoanalytic model, restorative theory, and adaptive theory.
Understand the activation-synthesis hypothesis: This theory suggests that dreams are the brain's attempt to make sense of random neural activity during sleep, essentially another form of thinking.
Consider the psychoanalytic model: This model, proposed by Freud, views dreams as a representation of unconscious desires and conflicts.
Evaluate the other options: Restorative theory and adaptive theory are not primarily focused on the cognitive process of dreaming, but rather on the functions of sleep itself.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)