Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
5. Consciousness and Sleep
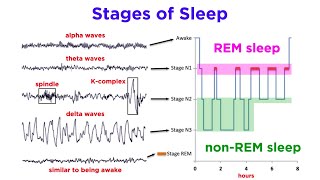
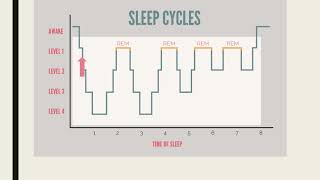
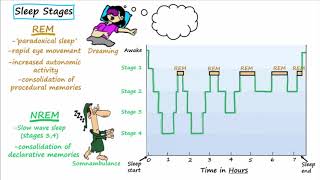
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Opium and its derivatives, morphine and heroin, duplicate the action of which of the following?
A
Serotonin
B
Endorphins
C
Melatonin
D
Cortisol
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
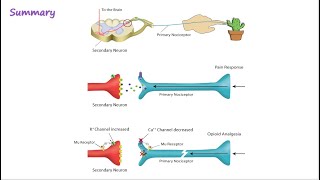
Understand the context: Opium and its derivatives, such as morphine and heroin, are known to affect the brain's chemistry and influence mood and perception.
Identify the function of endorphins: Endorphins are neurotransmitters in the brain that act as natural painkillers and mood enhancers. They are released in response to stress or discomfort and help to alleviate pain and induce feelings of pleasure or euphoria.
Compare the effects: Opium and its derivatives mimic the effects of endorphins by binding to the same receptors in the brain, which leads to pain relief and feelings of euphoria, similar to the natural effects of endorphins.
Differentiate from other options: Serotonin, melatonin, and cortisol have different roles. Serotonin is involved in mood regulation, melatonin regulates sleep-wake cycles, and cortisol is a stress hormone. None of these directly duplicate the pain-relieving and euphoric effects of opium derivatives.
Conclude the comparison: Since opium and its derivatives mimic the action of endorphins by binding to the same receptors and producing similar effects, the correct answer is that they duplicate the action of endorphins.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)