Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
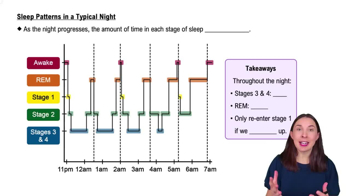
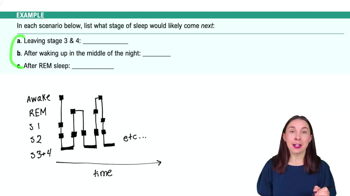
5. Consciousness and Sleep
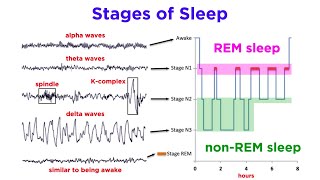
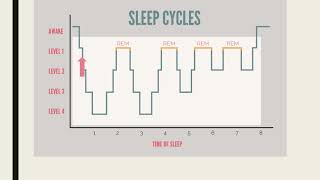
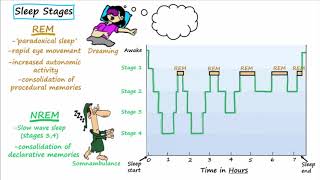
Sleep
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
A person with sleep apnea
A
stops breathing for 10 seconds or more.
B
falls asleep without warning.
C
experiences a state of panic.
D
gets up and walks around while still sleeping
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the definition of sleep apnea: Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or periods of shallow breathing during sleep.
Identify the key symptom of sleep apnea: The most common symptom is the cessation of breathing for at least 10 seconds, which can occur multiple times during the night.
Differentiate sleep apnea from other sleep disorders: Narcolepsy involves falling asleep without warning, while sleepwalking involves getting up and walking around while still asleep.
Recognize the physiological impact: During an apnea event, the lack of oxygen can lead to a state of arousal, causing the person to wake up briefly to resume breathing.
Consider the consequences: Frequent interruptions in breathing can lead to fragmented sleep and result in excessive daytime sleepiness and other health issues.

 3:25m
3:25mWatch next
Master Circadian Rhythms with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















































































![Race, Genes and IQ Differences | Bret Weinstein [Mini Clip]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/IztL_m3pd70/mqdefault.jpg)