Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
1. Introduction to Psychology
Early Schools of Thought
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
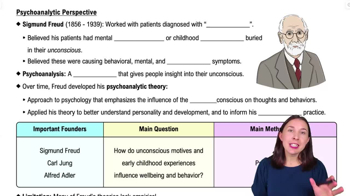
Freud believed that a number of things could lead to hysteria (or hysteria-like symptoms). Which of the following concepts did Freud NOT focus on?
A
Cultural context.
B
Childhood trauma.
C
Mental conflicts.
D
Unconscious thoughts and desires.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding the context of Freud's theories. Sigmund Freud was a pioneering figure in psychology, known for his development of psychoanalysis.
Recognize that Freud's work primarily focused on the internal psychological processes rather than external factors. His theories often revolved around the unconscious mind, childhood experiences, and internal conflicts.
Identify the key concepts Freud emphasized: unconscious thoughts and desires, childhood trauma, and mental conflicts. These were central to his understanding of psychological disorders, including hysteria.
Consider the concept of 'Cultural context.' Freud's theories were less focused on cultural or societal influences and more on individual psychological processes.
Conclude that 'Cultural context' is the concept Freud did not focus on in his explanation of hysteria, as his work was more centered on internal psychological dynamics rather than external cultural factors.

 5:44m
5:44mWatch next
Master Structuralism with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice