Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
4. Sensation and Perception
Visual Anatomy
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
In his theories of development, Jean Piaget focused primarily on
A
nurture.
B
the child's internal cognitive development.
C
the influence of other people on a child's development.
D
the crises that occur at each of eight stages of psychosocial growth.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Begin by understanding Jean Piaget's primary focus in his theories of development. Piaget was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development.
Recognize that Piaget's theory is centered around cognitive development, which refers to the internal processes of the mind and how children acquire knowledge.
Piaget proposed that children go through a series of stages of cognitive development, each characterized by different ways of thinking and understanding the world.
Understand that Piaget's theory emphasizes the child's active role in their own development, suggesting that children construct knowledge through interactions with their environment.
Differentiate Piaget's focus from other developmental theories, such as those emphasizing social influences or psychosocial crises, to clarify that his primary concern was the child's internal cognitive processes.

 3:08m
3:08mWatch next
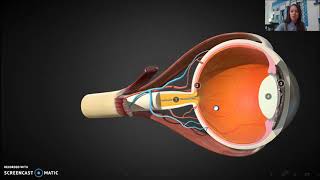
Master Anatomy of the Eye with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice















![The Human Eye & Color Blindness [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 3] (3.3)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Mwq23JTBnN0/mqdefault.jpg)



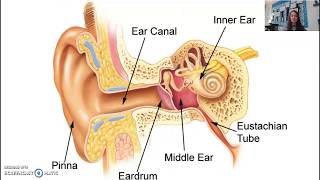

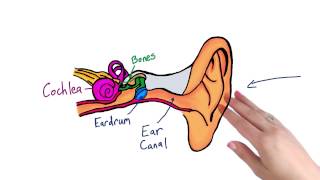



![The Process Of Smelling & Tasting [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 6] (3.6)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/vIQf0QAJFQA/mqdefault.jpg)




![Sensation of Touch, Layers of Skin & Pain [AP Psychology Unit 3 Topic 7] (3.7)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/sjbg9pf9Cj8/mqdefault.jpg)

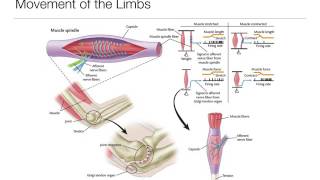






















![Factors affecting perception - Perception, GCSE Psychology [AQA]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ot4AjaQUo3Y/mqdefault.jpg)
![Social & Cognitive Factors In Learning [AP Psychology Unit 4 Topic 4] (4.4)](https://img.youtube.com/vi/Z1NIcVXplFk/mqdefault.jpg)