Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning41m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology33m
- 11. Personality48m
- 12. Social Psychology41m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders44m
- 15. Treatment47m
2. Psychology Research
Intro to Research Methods
Struggling with Psychology?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
Which of the following practices might improve the internal validity of an experiment?
A
Random assignment.
B
Providing participants with feedback about their performance.
C
Using a representative sample.
D
Increasing the sample size.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
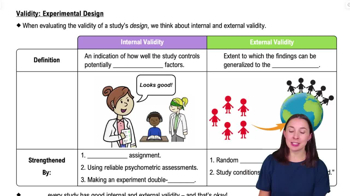
Understand the concept of internal validity: Internal validity refers to the extent to which an experiment accurately establishes a causal relationship between variables, free from confounding factors.
Identify the role of random assignment: Random assignment is a technique used to ensure that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group in the experiment, which helps control for confounding variables and increases internal validity.
Evaluate the impact of feedback: Providing participants with feedback about their performance does not directly affect internal validity, as it does not control for confounding variables or ensure causal relationships.
Consider the use of a representative sample: While using a representative sample is crucial for external validity (generalizability), it does not directly improve internal validity, which focuses on the causal relationship within the study.
Assess the effect of sample size: Increasing the sample size can improve the reliability of the results but does not directly enhance internal validity unless it helps in better randomization and control of confounding variables.

 1:46m
1:46mWatch next
Master Roadmap of the Lesson with a bite sized video explanation from Hannah Gordils
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice